
What is it?
It is a pathogen whose single virion (virus particle) is about 80 nanometers in diameter (0.00000003937 of an inch).
How it works
Coronavirus, or COVID-19, attacks the human respiratory system with spikes that attach to the surface of cells that line the inside of the lungs. By hijacking its host cells, the virus RNA enters the cell and sets off a chemical change that fuses the virus to the cell, and uses the host cell’s protein-making machinery to rapidly create new copies of the virus. In just hours, a single host cell can be forced to produce tens of thousands of new virions, which then go on to infect other healthy cells.
How Does it Make People Sick?
- Fuses the virus to cells on the cilia and other lung tissue surfaces
- As these sticky virion cells close down normal cell function, oxygen delivery stops
- Weakened immune system allows secondary infections to take hold
Between 3% and 17% of all COVID-19 patients require a ventilator to supply oxygen that is cut off by coronavirus cells. Unless the hyper inflammation resulting from these viral cells is reduced, the body shuts down. Secondary infections that take advantage of the weakened immune system are another cause of death.
Where Does it Come From?
Like SARS, AIDS, and Ebola, COVID-19 is a zoonotic disease. It jumped from another species to human hosts, probably in Wuhan China in late 2019. Best guess is it moved from bats to pangolins, an exotic species sometimes eaten as a delicacy, and then on to humans.
How Does it Spread Among Humans?
The most common form of transmission: Human-to-human via respiratory droplets.
The most common way that this illness spreads is through close contact with someone who has the infection. Close contact is around 6 feet but can be up to 16 feet with propelled droplets.
The disease is most contagious when a person’s symptoms are at their peak. However, it is possible for someone without symptoms to spread the virus. A study published January 7, 2021, and cited by the CDC concludes that over half of all COVID transmission comes from people who have no symptoms. (JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(1):e2035057. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.35057)
Droplets containing the virus can also land on nearby surfaces or objects. Other people can pick up the virus by touching these surfaces or objects. Infection can occur if the person then touches their nose, eyes, or mouth.
How Are Respiratory Droplets Transmitted?
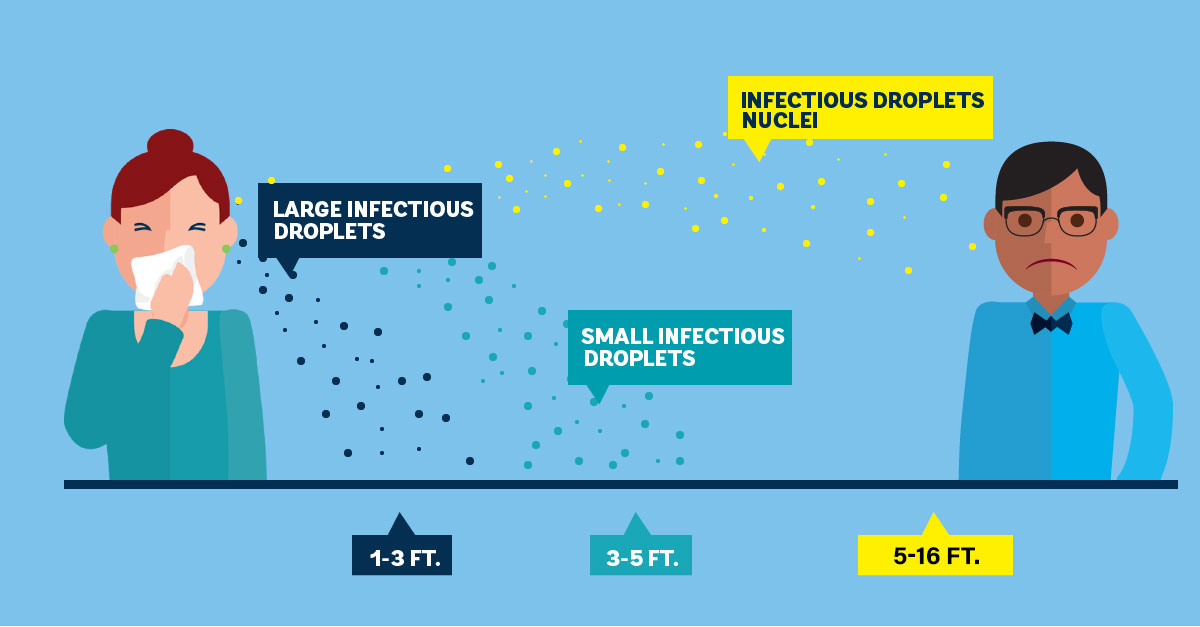
- Talking, laughing, shouting, singing, coughing, sneezing…. All activities that “spray” droplets.
- Coughing or sneezing into one’s hand can pass the droplets to surfaces (door handles, telephone, handrails) or to another person touched by that hand (use the elbow bump)
- Droplets containing the virus can also land on nearby surfaces or objects. Other people can pick up the virus by touching these surfaces or objects. Infection is likely if the person then touches their nose, eyes, or mouth.
- The serial interval is the time between one person developing the symptoms of a condition and a second person becoming infected and developing symptoms — thought to be approximately 4 days.
- The disease is most contagious when a person’s symptoms are at their peak. However, it is possible for someone without symptoms to spread the virus.
The COVID virus induces a hyperinflammatory response in the lungs. So we need a super inflammation fighter!
Enter — Cannabidiol – CBD!
How Does CBD Treat COVID-Induced Disease?
- CBD shares 20 protein targets common to inflammation-related pathways
- COVID-19 is linked to the rapid and prolonged surge of inflammatory cytokines (the cytokine storm in ARDS). CB2 receptors are a primary target of CBD receptor stimulation and they fight inflammation.
- CBD is a powerful immune regulator, “not pushing the gas pedal and not pushing the brake completely” = homeostasis, a balancing of the body’s regulatory systems.
- Questions remain and further research is coming: Dose-response, CBD alone or in combo w/other phytocannabinoids, timing (relative to the stage of fibrotic lung damage)
Effective vs Ineffective Ways to Beat COVID-19
- Safe, community-wide anti-transmission practices — works when used in a standardized, consistent, nationally implemented protocol*
- Blood serum from people who have recovered from the virus — not seen the numbers yet to conclusively say this creates immunity to SARS-CoV-2
- Herd immunity — requires massive exposure and a willingness to accept a substantial number of deaths while it is being accumulated
- Hydroxychloroquine — was used to fight malaria; not effective against COVID
- The Misinformed Approach: Don’t wear a mask or SIP or keep social distancing since these all infringe on your individual “freedom” — however since you can carry it without being symptomatic, this approach threatens vulnerable members of your community
- Vaccine – Current efforts create a vaccine by copying genetic material from a virus and add it to artificial nanoparticles vs from the virus itself. (Moderna)
Initially, countries that could react quickly to crises and had high levels of emergency preparedness ranked highest. Now countries with resilient economies are ranking higher.
How long does the coronavirus stay alive on surfaces?
- CDC has emphasized that it “does not spread easily” from surface contact, it’s still important to uncover how long the virus can survive on common surfaces
- up to 4 hours on copper, up to 24 hours on cardboard, and up to 2-3 days on plastic and stainless steel
- The CDC states, “Although the virus can survive for a short period on some surfaces, it is unlikely to be spread from domestic or international mail, products, or packaging. However, it may be possible that people can get COVID-19 by touching a surface or object that has the virus on it and then touching their own mouth, nose, or possibly their eyes, but this is not thought to be the main way the virus spreads.”

One way to treat COVID-19 that you won’t hear about in mainstream media
- Researchers randomly assigned 76 people with moderate to severe C19 into the vaccine group (50 patients) or no-vaccine (26 patients) group on the day they entered the hospital.
- * NO VACCINE GROUP: 13 out of 26 patients (50%) were admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU), and two died in the end.
- * VACCINE GROUP: Only 1 person out of 50 (just 2%!) required ICU admission, and NOT ONE PERSON died!
- This vaccine led to a 93% reduction in odds of ICU admission!
- What was the vaccine that was given in this study? Vitamin D
What can we take to treat COVID?
- Elderberry (liquid, tastes yummy)
- Echinacea (tincture, tastes not so yummy, but so effective!)
- Vitamin C
- Zinc
- Vitamin D
- CBD!!!
Seniors: A Most Vulnerable Population
- Older adults and people who have certain underlying conditions like heart or lung disease or diabetes are at increased risk of severe illness from COVID-19 illness.
- As you get older, your risk for severe illness from COVID-19 increases, with people over 85 at the greatest risk of all age groups.
How does this relate to Cannabis use?
- Seniors are the fastest-growing demographic of cannabis users, with a 250% increase in cannabis use among adults 65 and older in 2017.
- Taking CBD prophylactically for COVID is not a bad idea.
Prevention Tips
Avoiding close contact with sick individuals; frequently washing hands with soap and water; not touching the eyes, nose, or mouth with unwashed hands; and practicing good respiratory hygiene.

Wear a mask

Wash your hands

Don’t touch your eyes, nose or mouth

Stay home



Leave A Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.